By Noah Ibrahim
Urbanization is a population shift from rural to urban areas, “the gradual increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas”, and the ways in which each society adapts to the changes. The world in the 20th century experienced an outstanding increase in urbanisation population, people tend to migrate from towns to the cities in other to better their living conditions.
Based on nationally-collated census figures, combined with the UN estimates in 1960 twice as many people lived in rural settings (2 billion) than in urban areas (1 billion). In 2007, urban and rural populations were almost exactly equal at 3.33 billion each. In 2016, urban populations increased to 4 billion; while the world’s rural population had increased only marginally to 3.4 billion. UN estimates, therefore, report that 54 per cent of people in the world lived in urban areas in 2016. Using UN Urbanization Prospects projections, in 2018 this is estimated to be just over 55 per cent of the world.
With particular reference to Nigeria, it has been revealed by studies that migration of people from rural areas to cities in search of a better life, is the factor responsible for the rapid and continuous growth of urbanization in recent years. Nevertheless, meeting the needs of the increasing urban population is the sole reason why developers in the real estate sector have the urgent need to bring about an effective provision of affordable housing, thereby meeting the needs of housing and helping to solve most of the problems of urbanization in Nigeria.
From the research gathered from Empirical studies about 75% of the urban settlers live in slums and improper housing, which is in contrast to human dignity. This study aims to discuss urbanisation and the importance of affordable housing in Nigeria
An Overview of Urbanisation
One of the oldest global phenomena which is currently shaping the way to live is urbanisation, there are no countries in the world which do not experience urbanisation in different forms. Urbanisation has been defined as the increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities as against rural areas. It is the gradual increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas”, and the ways in which each society adapts to the change. According to the Demographic Partitions (2013), urbanization can be described as the “process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin living and working in central areas”
There has been an alarming trend and pattern of urbanisation in Nigeria, towns and cities have grown phenomenally because of the high rate of migration. In Nigeria, the pace of urbanization has been dramatic showing extraordinarily high rates of 5-10 percent per annum. The erection of factories and industries in the cities has caused people to abandon rural dwelling and move to the cities, thus, the need for affordable housing to cater to the needs of this growing population.
According to the Federal Mortgage Bank of Nigeria ( FMBN), the present housing deficit is at N22million contrary to the previous statistics of N 17 million. The world bank has estimated that it would cost Nigeria as high as N59.9trillion to bridge the housing deficit in Nigeria.
URBANISATION IN NIGERIA
In the last five decades, Nigeria has been experiencing urbanization. This is owing to rapid urban growth associated with natural population growth and rural-urban migration driven by rapid socio-economic changes and development. Prior to the colonial era, Nigeria encompassed various cities which varies uniquely in size and importance. During this era, the majority of people focused more on agriculture as their source of lively hood thus, reducing the rate of migration from the rural areas to the cites. The quest for a better life increased the pace at which people migrated to the cities from the rural areas during the 1960s ( post-independence). In 2019, the urban population for Nigeria was 51.2 %. Over the last 50 years, the urban population of Nigeria grew substantially from 17.8 to 51.2 % rising at an increasing annual rate that reached a maximum of 3.19% in 1981 and then decreased to 1.61% in 2019.
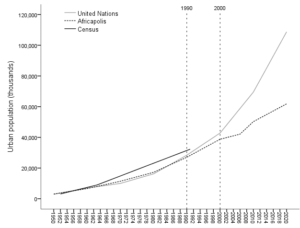
Figure 1.
Chat representing the decrease and increase in urban population
With the establishment of industries and factories in major cities in Nigeria, urbanisation is and would be on a constant rise. Overpopulation would be a major set back. As people keep moving into the cities the social infrastructures are not increasing with the number of people coming in every day because of this decent and affordable accommodation is not always accessible leading to overcrowding and an increase in slum life. A slum is defined by the UN-Habitat as “a heavily populated urban area characterized by substandard housing and squalor”

Figure 2.
Picture of a slum in Lagos Nigeria.
The significant rise in the population and size of Nigerian cites has lead to an acute shortage of dwelling units, resulting in overcrowding and exorbitant rate of housing rents. In 1991, the National Housing Policy (FRN, 1991) projected the urban housing shortage to be about 5 million housing units while the rural housing shortages stood at 3.2million.
Responding to this enormous problem, UN-Habitat advocates a twin-track approach that centres around improving, improving the supply and affordability of new housing through the supply of serviced land and housing opportunities at scale, which can control the development of new slums by widening housing choices and enabling the provision of housing opportunities at an appropriate scale, prices and diversity.
THE NEED FOR AFFORDABLE HOUSING
Housing is one of the three fundamental human basic needs of every citizen of a country. The Nigeria National Housing Policy defines ‘Housing’ as the process of providing functional shelter in a proper setting in a neighbourhood, supported by sustainable maintenance of the built environment for the day-to-day living and activities of individual and families within the communities.
Provision of affordable housing would initiate a significant development as it would provide shelter for people and also bring about infrastructural development, thus, meeting the social needs of the populace. There would be a provision of jobs for both skilled and unskilled labour as there would be a rise in the activities of the housing and building industry.
Housing is very sacrosanct to the economic and social framework in a nation like Nigeria. This is owing to the fact that it accommodates the smallest unit of its society, which is regarded as the family.
Evidently, there is an increasing rise in the housing deficit. According to the Federal Mortgage Bank of Nigeria ( FMBN), the present housing deficit is at N22million contrary to the previous statistics of N 17 million. The world bank has estimated that it would cost Nigeria as high as N59.9trillion to bridge the housing deficit in Nigeria.
The Nigerian population is at 204,394,025 of which the urban population is 52.0%. Over 90% of the country’s population are of the no/low-income groups. The present Gross Domestic Product (GDP) equals US$405.10 billion presently nonetheless; the Per Capita Income is very low at US$2457.80 as lastly recorded in 2016 which indicates clearly the fact that there is an unequal distribution of wealth as people’s income is not commensurate with the economic growth.
In the formal housing sector estimated an output of no more than 100,000 per year to an optimistic 200,000 per year, which covers only a fraction of the at least 700,000 units required per year to keep up with growing population and urban migration.
Further, most new housing production caters to upper-income households, leaving an acute housing shortage for middle and lower-income households. The greatest need for affordable housing is lower-income households in urban areas. Almost 50% of the Nigerian population lives in cities and about 80% of this urban population lives in substandard conditions.
CONCLUSION
Nigeria is faced with a high rate of urbanisation just like other developed countries, there are many negative effects of urbanisation and this is hinged greatly on the housing deficit which would be on a constant increase because it is not affordable for a large number of the Nigerian populace. Thus, it has been identified that it is important to provide the availability of affordable housing by effectively committing to the delivery of housing facilities that are affordable and accessible to Nigerians, most importantly to those within the low-income and medium-income group. Achieving Affordable housing would not only provide a suitable and accessible living for low-income earners but it would also increase house ownership, expand the construction sector and the mortgage market. In addition, there would be a significant decrease in poverty level and also increase the quality of life of the citizens and their productivity
SOURCE:
Our world in data.
Definition of urbanisation
The housing deficit of Nigeria
The present Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as lastly recorded in 2016
The Nigerian population
Noah Ibrahim is a young, innovative entrepreneur and real estate professional and is the MD/CEO of Novarick homes and properties. To get more insightful views by Noah Ibrahim visit his blog www.noahibrahim.org

